Code metrics are the measurement scales and methods used in software testing, and Cyclomatic complexity is one example of a code metric used in static testing. When performing static code analysis, code metrics can be used to calculate numerous attributes of the code such as comment frequency, depth of nesting, cyclomatic number and number of lines of code. Code metrics can not only compute these attributes but can also be done as the design and code are being created and as changes are made to a system, to see if the design or code is becoming bigger, more complex and more difficult to understand and maintain.
Cyclomatic complexity is a code metric used on static testing when the testers take all of the expected statements and decisions and compile them into a diagram or map of the system. It involves an equation defined by the ISTQB book as L-N+2P. L is the number of edges or lines connecting nodes, N is the number of nodes or steps in the process flow reached when decisions are made, P is the number of connected components (usually the entire process is connected and therefore this is usually equal to 1) and example of this is below.
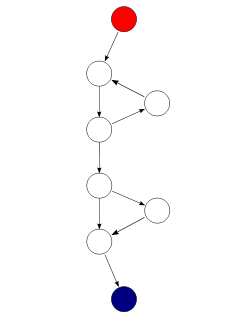
In this example there are 9 edges or lines, 8 nodes, and the entire thing is connected meaning P=1
the cyclomatic complexity equation would look like: 9-8+2*1=3
No comments:
Post a Comment